This web page is intentionally created with accessibility errors to demonstrate the functionality of automatic accessibility checkers for web pages. View this webpage in an accessibility checker (WAVE) to display alternative text and help identify accessibility issues.
Alternative Text
Alternative text, also known as alt text, is a textual substitute that provides the equivalent experience for everyone and must represent the image’s content or function.
Error Types: Errors must be fixed. Alerts should be fixed. These fixes, both errors and alerts, improve the accessibility and usability of the content. Accessibility checkers can provide false positives for an image’s alt text.
Important: It is important to check alt text manually. Accessibility checkers can only determine if you do or don’t have alt text. It can not tell you the quality of the alt text or if it is equivalent.
Best Practices: The alt text describes the image’s content or function succinctly. While decorative images don’t need alt text, most other images do need alt text. The alt text is determined by the image and its surrounding content.
Alt Text and Equivalent Experience
The alt text provides an equivalent substitute, whether you can see the image or not.
Image

Screen Reader
A screen reader will read the image as, “Graphic, A crimson WSU Cougar head on a light gray background.”
Missing Image
A missing image will have the browser’s broken image icon and the alt text.
Leave the image block as it is. I know it looks broken, but it isn’t for this demo purpose.
Image’s Function
The image’s function determines what to include in the alt text for the image. The alt text should describe the destination or function.
These examples demonstrate how an accessibility checker identifies a linked image.
Destination Alt Text

Important: This is a manual check. An accessibility checker will not determine if the alt text is appropriate for the linked image.
Important: Accessibility checkers cannot tell if the alt text describes the destination or the function. It is always a manual check to see if the alt text provides the correct information.
Context is Everything
The surrounding content helps determine what to include and what not to include in the alt text.
In these examples, you will see how the alt text changes based on the surrounding content.
Profile Page
Surrounding content: Professor Jane Smith’s profile web page

Academic Page
Surrounding content: Academic offerings on a department website. A professor is not mentioned on the webpage.

Academic Page with Additional Information
Surrounding content: Academic offerings on a department website, including courses. A professor is not mentioned on the webpage.

Important: A manual check determines if the alt text provides an equivalent experience. It is always a manual check to see if the alt text provides an equivalent experience. Accessibility checkers cannot tell if the alt text provides too little or too much information.
Suspicious Alt Text
Suspicious alt text contains non-essential words like “image of” or an alt text with a space. Or where the alt text matches another nearby image’s alt text.




Error: Alert
Best Practice: Alt text should not include “image of,” “photo of,” or “graphic of.” Alt text should be unique to include details that set it apart from other images.
Missing Alt Tag
A missing alt tag is not ignored by assistive technology, like a null or empty alt text is. Assistive technologies will read the file name when the alt tag is missing.

Error Type: Error
Note: The implementation of the image is such that the alt tag is missing.
Decorative Images
Decorative images do not add visual support or content to the surrounding content. If removed, nothing would be missing from the content. Assistive technology ignores an empty (or null) alt text.

Best Practice: When in doubt about whether an image is decorative or not, add the alt text anyway and provide equivalent information in the alt text, as it supports the surrounding content. See Context is Everything for more information..
Images with Text
The text in an image must be included in the alt text.
The text in an image that is more than 150 characters should be considered a complex image. It must be handled differently to include all the text in the image.

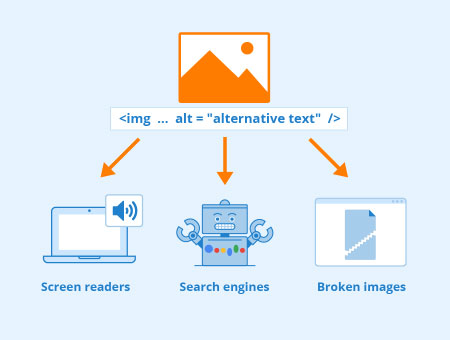
Error Type: Error
Best Practice: Include all the text in the image in the alt text. Try to keep the length to below 150 characters.
Complex Images
Complex images need more details in the alt text than the suggested 150-character limit. Use the caption, a nearby location, or a link to another location to accommodate the additional details.

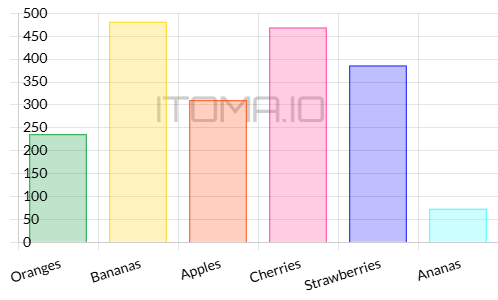
| Fruit | Amount |
|---|---|
| Oranges | 236 |
| Bananas | 482 |
| Apples | 310 |
| Cherries | 469 |
| Strawberries | 386 |
| Ananas | 72 |
Best Practice: The alt text includes a summary of the image and where to find the additional details.
Images in Motion

Images with motion must have a means to pause the image or animation.
An animated photo can serve a purpose. But, you can only use an animated photo if it last less than three seconds, or you can pause the animation.
Best Practice: Don’t use animated photos unless they can be paused or is less than 3 seconds and does not repeat.
Note: Animated photos or videos can not contain anything that flashes more than three times in any one second.
Accessibility Checks
This list of accessibility checks for Core Concept Images includes whether it is an automatic check or a manual check
- Image content or function is described with alternative text. [manual]
- Decorative images are implemented in a way that can be ignored by assistive technology. [automatic & manual]
- Complex images are described in detail. [automatic & manual]
- Text that is part of an image is duplicated as alternative text. [automatic & manual]
- Images with motion can be paused by the viewer. [manual]
Tools for Web Pages
- WAVE (website) and browser extensions: This is a full-page accessibility automatic check.
- Wave: Alternative text result documentation: These are the WAVE results associated with alternative text.
- Web Developer (Browser Add-on): This browser extension features an Images tab with a Display Alt Attributes option. The alt text for images is displayed below the image.
Want to check non-web page-based digital content? See the Digital Accessibility Testing/Scanning Tools web page for additional resources.
Additional Support
Analyze an Image’s Alt Text
When in doubt about an image needing alt text, add alt text.
What to include or not in the alt text is based the image subject and the surrounding content.
Consider these questions when deciding on the alt text.
- Is it providing enough information as it relates to the surrounding content?
- Is it too much information?
- Is it providing information in the alt text that isn’t supported by the surrounding content?
- Is it a decorative image?
- Does the image contribute meaning to the surrounding content?
- Is the image linked?
- Does the alt text describe the destination or function?
- Are the alt text and caption different?
- Is the alt text less than 150 characters?
Alt Text Decision Tree
Tools for deciding about the alt text to provide.
Resources
-
A guide to alt text across popular tools
Source: Pope Tech
In this article, we’ll list out several tools and give details about their alt text support and tips for the best way to add accessible images in the tool.
Tags: Article -
Accessibility and QR codes
Source: Terta Logical
Quick Response (QR) codes are graphics that can be scanned to direct people online to complete an action or find content. This blog post explores considerations and provides guidance for creating accessible experiences with QR codes.
Tags: Article -
Accessible building blocks for web: images
Source: TetraLogical
In this video, learn how to ensure that images on websites are easy to perceive and flow logically with the rest of the content. Also, discover the importance of clear and accurate text descriptions. By applying accessibility considerations to the building blocks of your web content you can create digital products that everyone can use.
Tags: Video -
Accessible QR Codes – The Ultimate Guide
Source: Access Lab
You may think that QR codes are great for securing your login, or letting users read more online about a product marketed in a news paper ad. But there is a high risk you are creating barriers for people with disabilities, unless you use QR codes correctly. This article is your ultimate guide to accessible QR codes!
Tags: Article -
Alt text decide-o-matic
Source: Scottish Enterprise Design blog
This interactive decision tree is based on the W3C’s alt text decision tree.
Tags: Tool -
Alt Text for Accessibility
Source: Level Access
The importance of alt text for accessibility (and beyond) with practical tips for writing it more effectively.
Tags: Article -
Alt Text: What to Write
Source: Nielsen Norman Group
Images are decorative, functional, or informative. Skip alt text for decorative. Describe the action for functional. Convey the message for informative.
Tags: Article -
Alternative text image types and when the alt attribute should be empty
Source: Pope Tech
Learn about the three types of images when it comes to alternative text and when the alt attribute should be empty.
Tags: Oct-2025, Video -
Alternative text in the wild: 5 alternative text examples
Source: Pope Tech
Writing alternative text seems straightforward – just add a description to an image. In this article, we’ll go through 5 alternative text examples found on real websites. We’ll explain why the example is right or could be better to help you make the best alternative text choices for your own images.
Tags: Article -
Fix alternative text issues using the free WAVE accessibility checker
Source: Pope Tech
We’ll use the free WAVE extension in this video to review alternative text.
Tags: Oct-2025, Video -
How to design great alt text: An introduction
Source: Deque
Images need alternative text (alt text). In order to write appropriate alt text, you need to understand who you’re writing the alt text for and the purpose of the image.
Tags: Article -
How to do alt text on social media for artists and photographers
Source: Nicholas Steenhout
Adding alt text on images you post on social media is important for blind people to access your content.
Tags: Article -
How to Make QR Codes More Accessible
Source: Vision Australia
As designers and communications professionals, we can make QR codes more accessible and user-friendly.
Tags: Article -
How to Write Alt Text for GIFs
Source: Veroniiiica (Veronica with Four Eyes)
Tips for writing alternative text for gifs.
Tags: Article -
How to write text descriptions (alt text) in BBC News articles
Source: BBC: Global Experience Language
This guidance is for staff who use digital images when creating content for BBC News.
Tags: Article -
Introduction to alternative text
Source: Pope Tech
Learn what alternative text is, where it goes, what the alt attribute is, and why the alt attribute is important.
Tags: Oct-2025, Video -
My Approach to Alt Text
Source: Adrian Roselli
An approach to writing alternative text for images. Writing alternative text is not a technical exercise (at least, not beyond basic WCAG conformance); it is copywriting tailored to your audience and constraints.
Tags: Article -
Top 10 Common Accessibility Issues in Websites
Source: AFixt
But despite good intentions, many websites fall short of compliance with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and laws like Section 508.
Tags: Article -
What alternative text is, when to use it, and how to write great alt text
Source: Pope Tech
Alternative text describes an image for users with visual disabilities. Every image needs an HTML alt attribute even if it’s empty, but not every image needs alternative text.
Tags: Article